
h or –human-readable: This prints out the file sizes in human readable form such as KB, MB or GB There are several command line options with du.
Using du commandĭu (short for Disk Usage) is a Linux command that allows you estimate disk space usage. If you want to see the “true” size of the folder, you will need to use the du command. This means that you are likely to see folders listed with a size of 4k rather than the sum of all its files and sub-folders. In Linux, the folders are nothing but files with some special properties. In order to list files inside the sub-directories inside the folder, you can use the -R optionĪlthough efficient in displaying the file sizes, it is not as good if you want the size of the “entire” folder. Using the above options, you can easily list the sizes of the files inside a folder R or –recursive : It displays the sub-folders recursively. h or –human-readable : prints the file sizes in human readable formats, such as KB, MB or GB etc l : uses the long listing format that displays several of the file metadata Let’s look at some of the command line options that are available with ls.
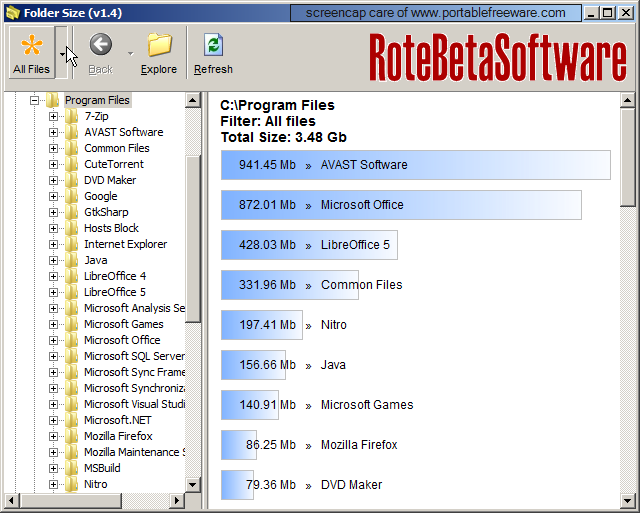
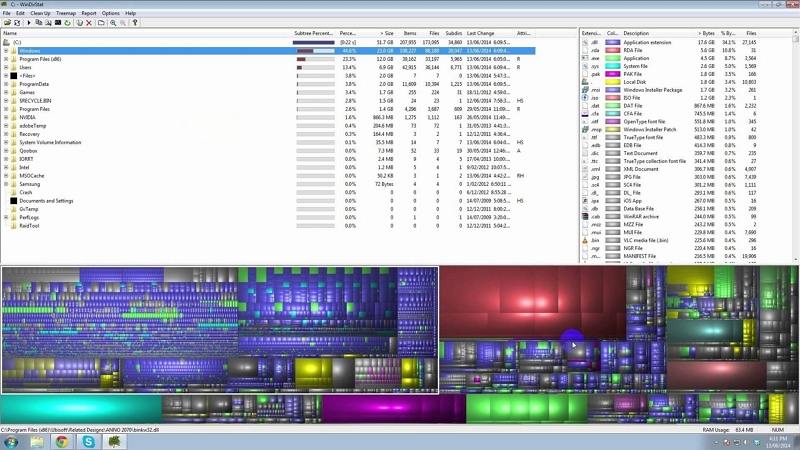
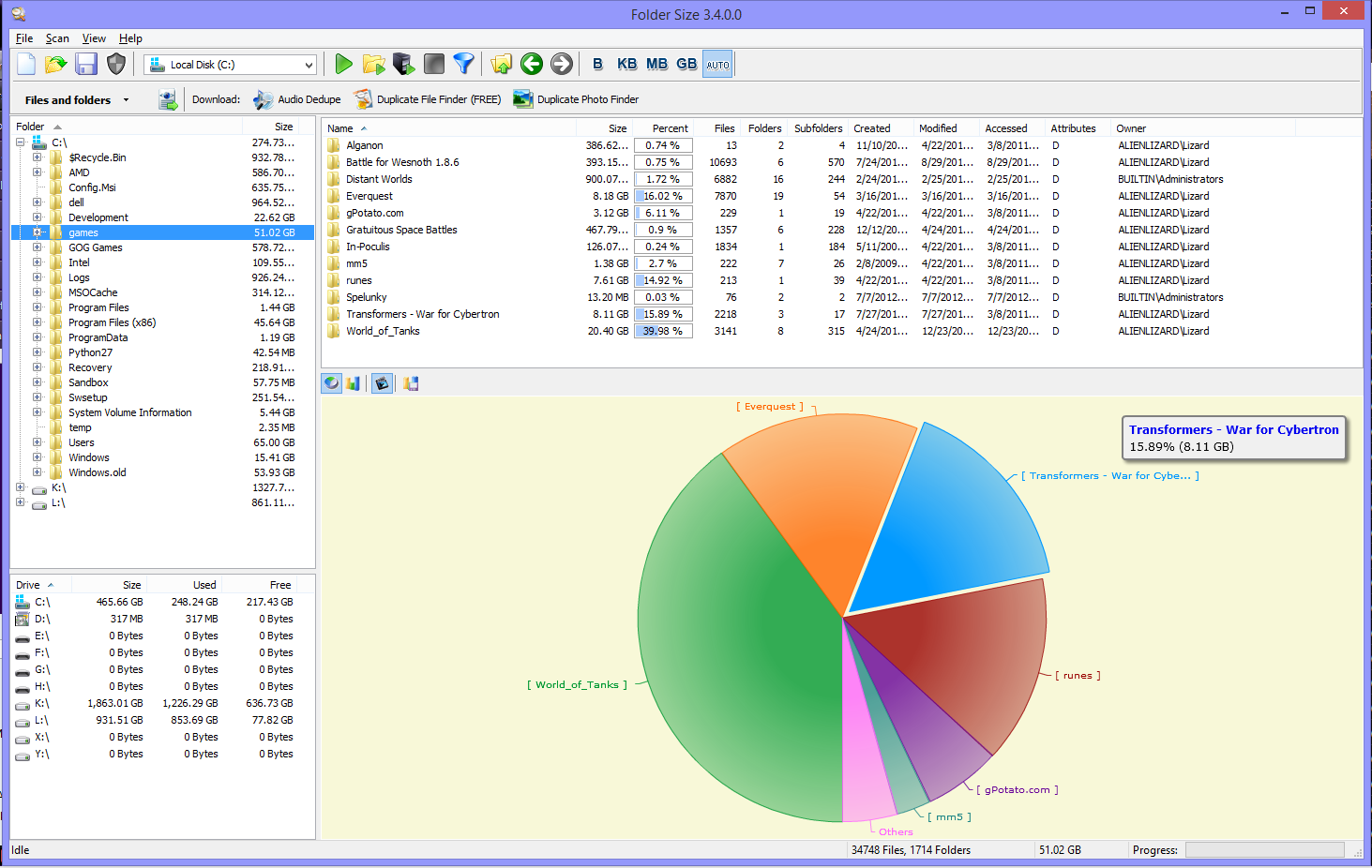
The ls command also can print many attributes and metadata information about the files it is listing. It is used to list the contents of a folder or directory. Ls is probably one of the widely used command that everybody knows. We will also look at some other utilities that let you do this graphically as well. There are primarily two commands that lets you do this: ls and du. And Linux is no exception.įirst, we will see how you can easily summarize the size of folders and sub-folders and files in Linux from the command line. Keeping your file system organized is just good practice and a tool to proper maintenance of your system. No matter what operating system you use, you routinely would want to know the size of folders, sub-folders and files on your file system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
